All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
Summer Scorcher Predicted, Again! Double Glazed ... in East Victoria Park Western Australia
Glazing merely indicates the windows in your house, including both openable and fixed windows, in addition to doors with glass and skylights. Glazing actually simply means the glass part, but it is normally used to refer to all elements of an assembly including glass, films, frames and home furnishings. Focusing on all of these elements will help you to attain effective passive design.

Energy-efficient glazing makes your house more comfortable and significantly minimizes your energy costs. However, unsuitable or improperly developed glazing can be a significant source of undesirable heat gain in summertime and significant heat loss and condensation in winter season. Approximately 87% of a home's heating energy can be acquired and up to 40% lost through windows.
Why Do You Need Double Glazing Windows In Summer? in Joondalup Western Australia
Glazing is a considerable investment in the quality of your house. A preliminary investment in energy-efficient windows, skylights and doors can greatly decrease your yearly heating and cooling expense.

This tool compares window choices to a base level aluminium window with 3mm clear glass. Understanding a few of the crucial properties of glass will assist you to select the finest glazing for your house. Secret homes of glass Source: Adjusted from the Australian Window Association The quantity of light that goes through the glazing is understood as visible light transmittance (VLT) or visible transmittance (VT).
Home Window Glazing - Sustainability Victoria in Pearsall WA
The U worth for windows (revealed as Uw), describes the conduction of the whole window (glass and frame together). The lower the U worth, the higher a window's resistance to heat circulation and the better its insulating worth.
For example, if your home has 70m2 of glazing with aluminium frames and clear glass with a U value of 6. 2W/m2 C, on a winter season's night when it is 15C cooler outside compared to inside, the heat loss through the windows would be: 6. 2 15 70 = 6510W That is equivalent to the overall heat output of a large room gas heater or a 6.
Double Glazed Windows: A Complete Guide in Walliston Western Australia
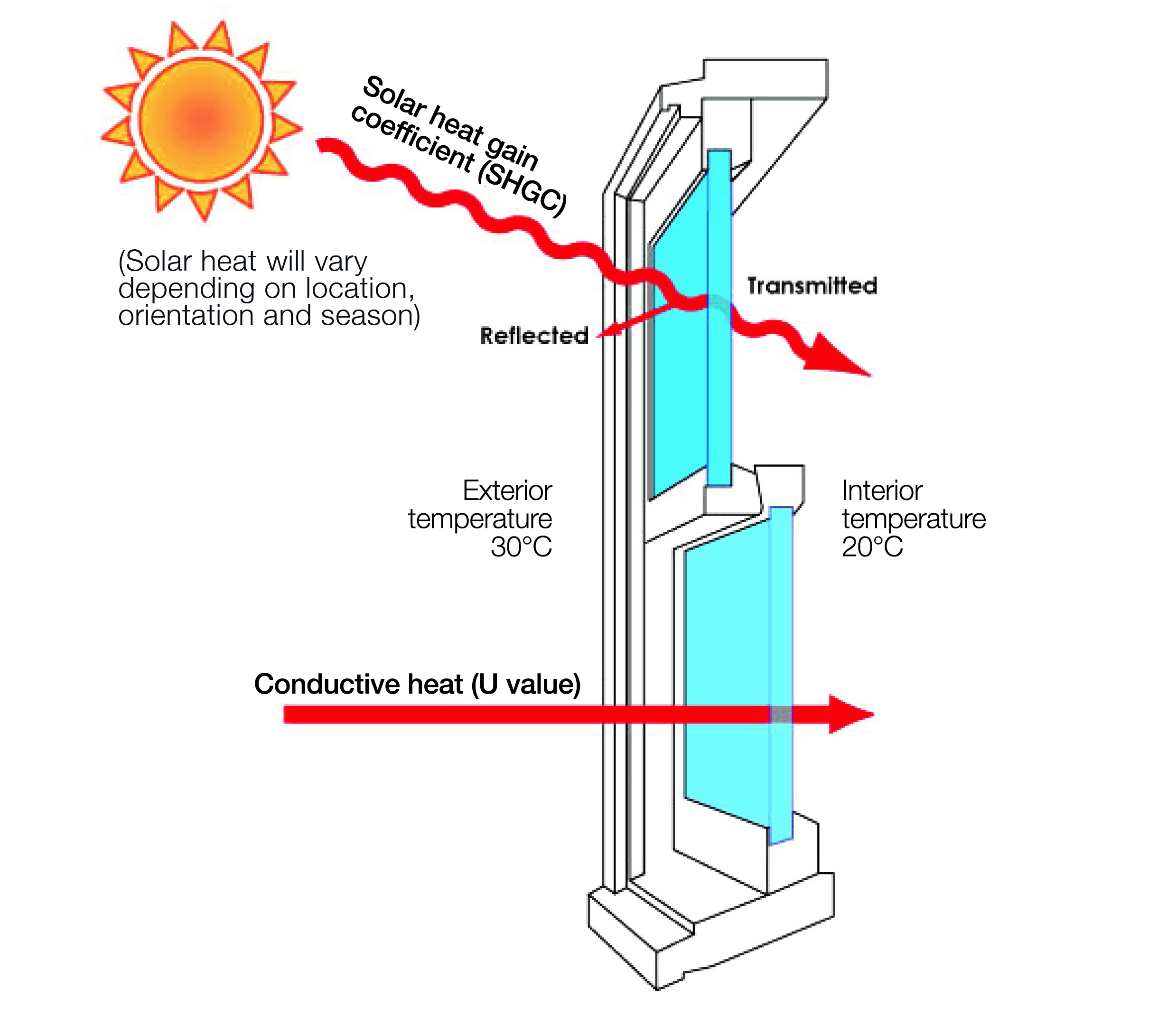
If you choose a window with half the U value (3. 1W/m2 C) (for instance, double glazing with an argon-filled space and less-conductive frames), you can halve the heat loss: 3. 1 15 70 = 3255W The solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) for windows (expressed as SHGCw) measures how readily heat from direct sunshine flows through a whole window (glass and frame together).
The lower a window's SHGC, the less solar heat it transmits to your house interior. Glazing producers state an SHGC for each window type and style. The actual SHGC for windows is impacted by the angle that solar radiation strikes the glass. This is called the angle of incidence.
Keep Cool This Summer Without Overusing Your Aircon. in Mosman Park Perth
When the sun is perpendicular (at 90) to the glass, it has an angle of incidence of 0 and the window will experience the maximum possible solar heat gain. The SHGC stated by glazing manufacturers is always calculated as having a 0 angle of occurrence. As the angle increases, more solar radiation is reflected, and less is transferred.
Latest Posts
Double Glazed Windows in West Leederville Perth
Double Glazed Windows Melbourne in Medina Western Australia
Double Glazing Companies Near Me Reviewed 2023 in Huntingdale WA